
Journal of Nutrition Research
An official journal of IAPEN India association



Journal of Nutrition Research
DOI: 10.55289/jnutres/v12i1_23.10
Year: 2024, Volume: 12, Issue: 1, Pages: 39-46
Original Article
Balasara Shisha Lyngdoh 1 , Ophelia Mary Kharmujai 2 , Caleb Harris ✉ 3 , Vikas Jagtap 4 , Herman Nadon 5 , Gwyneth Pde 1
Received Date:22 August 2023, Accepted Date:15 April 2024, Published Date:18 June 2024
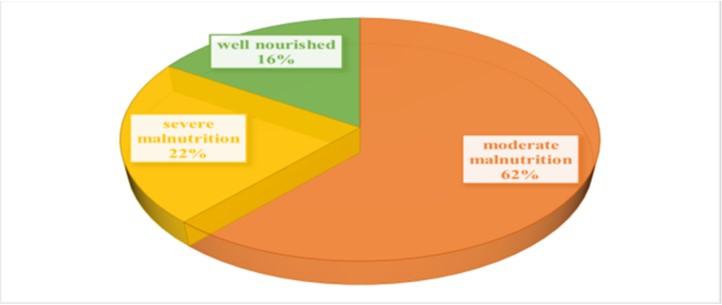
Patients with cancer often have poor nutritional status, which further deteriorates as the disease progresses. Systematic assessment of the nutritional status is essential to determine the nature of intervention required for each individual. This cross-sectional study was conducted at a tertiary care centre in Meghalaya, North East, India with the primary objective of assessing the nutritional status of cancer patients. The secondary objectives were to assess the diet pattern of cancer patients and the nutritional intervention, which was provided as per the nutritional status. A total of 100 patients who consented to participate were selected consecutively for this study and were interviewed by the first author. Patient Generated Subjective Global Assessment (PGSGA) parameters and other parameters like anthropometry, biochemical values and dietary pattern to assess the nutritional status were used. Majority of them (60%) had Gastrointestinal cancer. The nutritional status of the participants, using the PG-SGA Global Assessment Categories, indicated that 84% of the participants were suffering from moderate to severe malnutrition. An analysis of the weight loss showed that 38% of the participants had a weight loss of 20% or greater in the previous 6 months. The diet pattern of the participants clearly indicated a decrease in the frequency of consumption of dietary fibre derived from wholegrains, whole grams and fruits. The study findings also revealed that 75% of the participants had an altered food intake pattern. As per the PGSGA parameter of symptoms which have an impact on nutritional intake, 40% of the participants were not feeling up to most things, but in bed or chair less than half a day. Based on these data regarding the food intake, nutritional related symptoms and the rate of activity, it clearly indicates that most of the participants were malnourished. Nutritional intervention should be provided to all cancer patients once they are diagnosed in order to prevent the severity of malnutrition.
Keywords
Nutritional Status in Cancer, Patient Generated Subjective Global Assessment, Diet pattern, Northeast India, Malnutrition in cancer
© This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Published By India Association for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition (IAPEN)
Subscribe now for latest articles and news.